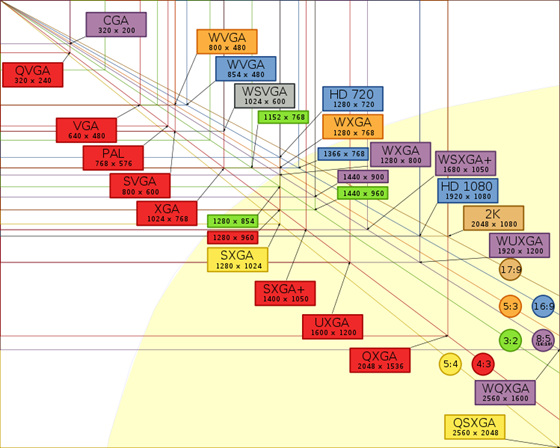
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixelsin each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube (CRT), flat panel or projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays.
It is usually quoted as width × height, with the units in pixels: for example, "1024×768" means the width is 1024 pixels and the height is 768 pixels. This example would normally be spoken as "ten twenty-four by seven sixty-eight" or "ten twenty-four by seven six eight".
One use of the term “display resolution” applies to fixed-pixel-array displays such as plasma display panels (PDPs), liquid crystal displays (LCDs), digital light processing (DLP) projectors, or similar technologies, and is simply the physical number of columns and rows of pixels creating the display (e.g., 1920×1080). A consequence of having a fixed grid display is that, for multi-format video inputs, all displays need a "scaling engine" (a digital video processor that includes a memory array) to match the incoming picture format to the display.
Note that the use of the word resolution here is a misnomer, though common. The term “display resolution” is usually used to mean pixel dimensions, the number of pixels in each dimension (e.g., 1920×1080), which does not tell anything about the resolution of the display on which the image is actually formed: resolution properly refers to the pixel density, the number of pixels per unit distance or area, not total number of pixels. In digital measurement, the display resolution would be given in pixels per inch. In analog measurement, if the screen is 10 inches high, then the horizontal resolution is measured across a square 10 inches wide. This is typically stated as "lines horizontal resolution, per picture height;"[citation needed] for example, analog NTSC TVs can typically display 486 lines of "per picture height" horizontal resolution, which is equivalent to 648 total lines of actual picture information from left edge to right edge. Which would give NTSC TV a display resolution of 648×486 in actual lines/picture information, but in "per picture height" a display resolution of 640×480.
| Width | Height | % of Internet Users |
|---|---|---|
| 1024 | 768 | 22.63 |
| 1366 | 768 | 15.63 |
| 1280 | 800 | 14.55 |
| 1280 | 1024 | 7.96 |
| 1440 | 900 | 6.92 |
| 1680 | 1050 | 3.75 |
| 1920 | 1080 | 3.70 |
| 1600 | 900 | 3.12 |
| 1360 | 768 | 2.65 |
| 1024 | 600 | 2.37 |
| 1152 | 864 | 1.91 |
| 1280 | 768 | 1.84 |
| 1280 | 720 | 1.66 |
| 800 | 600 | 1.44 |
| 1920 | 1200 | 1.04 |
| 1280 | 960 | 0.86 |
| 768 | 1024 | 0.80 |
| 1093 | 614 | 0.54 |
| 1024 | 640 | 0.28 |
| 1152 | 720 | 0.26 |
| Other | 6.08 |
| Code | Name | Aspect ratio | Width | Height | % of Steam users |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XGA | eXtended Graphics Array | 4:3 | 1024 | 768 | 5.12% |
| XGA+ | eXtended Graphics Array Plus | 4:3 | 1152 | 864 | 1.04% |
| WXGA | Widescreen eXtended Graphics Array | 16:9 | 1280 | 720 | 0.69% |
| WXGA | Widescreen eXtended Graphics Array | 16:10 | 1280 | 800 | 5.28% |
| SXGA (UVGA) | Super eXtended Graphics Array | 4:3 | 1280 | 960 | 0.95% |
| SXGA | Super eXtended Graphics Array | 5:4 | 1280 | 1024 | 11.80% |
| HD | High Definition | 16:9 | 1360 | 768 | 1.42% |
| HD | High Definition | 16:9 | 1366 | 768 | 6.50% |
| WXGA+ | Widescreen eXtended Graphics Array Plus | 16:10 | 1440 | 900 | 9.20% |
| HD+ | High Definition Plus | 16:9 | 1600 | 900 | 4.05% |
| UXGA | Ultra eXtended Graphics Array | 4:3 | 1600 | 1200 | 0.81% |
| WSXGA+ | Widescreen Super eXtended Graphics Array Plus | 16:10 | 1680 | 1050 | 18.01% |
| FHD (Full HD) | Full High Definition | 16:9 | 1920 | 1080 | 21.78% |
| WUXGA | Widescreen Ultra eXtended Graphics Array | 16:10 | 1920 | 1200 | 7.80% |
| QFHD | Quad Full High Definition | 16:9 | 2560 | 1440 | 0.65% |
| Other | 4.92% |