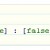
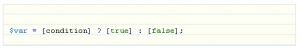
In addition to the enlarged if – else statement that you will use in most cases, there is also a short structure for an if – else statement. This format uses the so-called “ternary operator ‘. The syntax of this shorthand structure is as follows:
$var = [condition] ? [true] : [false];
- Condition = The condition which must be met.
- True = Executed if the condition is met.
- False = Executed if the condition failes.
Thus, the above statement means the same as this enlarged structure:
<?php
if (condition) {
$var = [true];
} else {
$var = [false];
}
?>
Examples
Let’s take a look at some example.
Filled in a name?
<?php $name = isset($_POST['name'])?$_POST['name']:'Unknown'; // If $_POST['name'] exists, we use that for the name, else we use Unknown. ?>
We can also use it to easily echo stuff:
<?php
$fruit = 'apple';
echo ('pear' == $fruit)?'pear':'apple';
// Will echo apple
?>
It is even possible to use php-functions inside it:
<?php
$input = 'Just a string to be hashed';
$hashMethod = 'sha1';
$hash = ('sha1' == $hashMethod)?sha1($input):md5($input);
// $hash will contain an sha1 hash of $input
?>
Conclusion
The short if-else structure is a good way to keep your code organized. However, it is not possible to use such a thing as: ‘elseif’.
I use it all the time to assign values to variables, with just one rule of code, I’m sure my vars have a proper value. Especially when using forms, this is a very useful function of PHP.